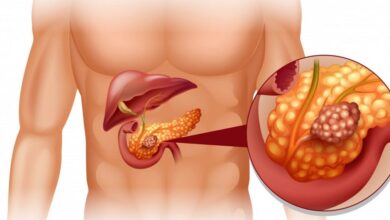
What is Cancer? Understanding the Disease That Affects Millions
Cancer is a term that often sparks fear, but understanding what it truly is can help demystify the condition. It’s a disease that touches almost everyone in some way, whether through personal diagnosis, a loved one, or even public awareness campaigns. This article will explore what cancer is, how it develops, and the broader implications of this complex disease.
Defining Cancer: A Closer Look at the Disease
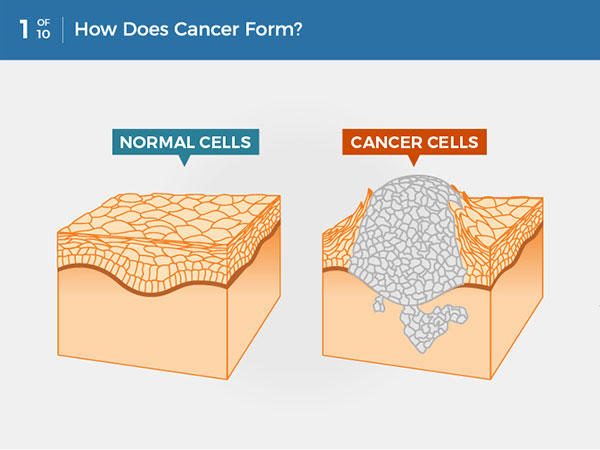
Cancer isn’t a single disease but rather a group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. These rogue cells can invade nearby tissues and disrupt normal bodily functions. If left unchecked, cancer can spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body, making it harder to treat.
How Does Cancer Begin?
Cancer starts when genetic changes disrupt the normal processes that regulate cell growth and division. In a healthy body, cells grow, divide, and die in a controlled manner. However, when the DNA within a cell becomes damaged or altered, these processes can go haywire, leading to abnormal cell behavior.
For example, imagine the body as a highly organized city. In this city, each cell has a specific job, like a worker at a factory. When the worker ignores instructions and starts producing defective products, chaos ensues. That’s essentially what happens when cancerous cells take over.
Common Types of Cancer
There are over 100 different types of cancer, and they’re typically named after the organ or tissue where they originate. For example:
- Carcinomas: These originate in the skin or tissues lining internal organs.
- Sarcomas: Found in bones, muscles, or connective tissues.
- Leukemia: Affects blood-forming tissues like the bone marrow.
- Lymphomas: Begin in the lymphatic system.
Understanding the type of cancer is crucial for determining the best treatment approach.
What Causes Cancer? Exploring Risk Factors
Cancer doesn’t have a single cause; it results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While some risks are beyond our control, like inherited mutations, others are influenced by lifestyle choices.
Genetic Factors
Some people are predisposed to cancer due to genetic mutations passed down from their parents. For instance, BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancers. However, it’s important to remember that inheriting a mutation doesn’t guarantee you’ll develop cancer; it merely raises the likelihood.
Lifestyle Choices and Environmental Exposures
Tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of exercise are all lifestyle factors that can increase cancer risk. Additionally, environmental exposures like pollution, radiation, and carcinogenic chemicals can damage DNA and trigger cancerous growths.
Even everyday habits like sunbathing without sunscreen can contribute to skin cancer over time. This highlights the importance of making conscious, healthy choices to minimize risks.
How Is Cancer Diagnosed?
Early detection is one of the most critical factors in effectively treating cancer. Medical advancements have provided numerous tools for diagnosing the disease.
Common Diagnostic Techniques
- Imaging Tests: Techniques like MRI, CT scans, and X-rays help visualize abnormalities inside the body.
- Biopsies: A small sample of tissue is taken from the suspicious area and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Blood Tests: Certain cancers release markers into the bloodstream, which can be detected through specialized blood tests.
The Role of Regular Screenings
For certain types of cancer, like breast, cervical, and colorectal cancers, routine screenings can detect the disease in its early stages when it’s most treatable. Mammograms, Pap smears, and colonoscopies are just a few examples of preventive tools that save lives every day.
The Stages of Cancer: How Advanced Is It?
Once cancer is diagnosed, determining its stage is crucial for planning treatment. Staging describes how much cancer is in the body and whether it has spread.
The TNM System
Doctors commonly use the TNM system to stage cancer:
- T (Tumor): Size and extent of the primary tumor.
- N (Nodes): Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- M (Metastasis): Whether cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
Each factor is assigned a number, which helps classify the cancer into stages ranging from I (localized) to IV (advanced/metastatic).
Why Staging Matters
Understanding the stage helps doctors tailor treatments to the patient’s specific needs. For example, early-stage cancers may only require surgery, while advanced cases might need a combination of chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies.
Treatment Options: Fighting Cancer at Every Level
The good news is that advances in medical science have led to a wide range of treatment options. The choice of treatment depends on the type, stage, and location of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Standard Treatments
- Surgery: Removing the tumor is often the first line of defense.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs are administered to kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
Emerging Therapies
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth, sparing healthy cells.
- Hormone Therapy: Blocks hormones that fuel certain cancers, like breast or prostate cancer.
Palliative Care
For advanced cases, palliative care focuses on improving quality of life by managing symptoms and providing emotional support.
Living with Cancer: The Emotional and Social Impact
A cancer diagnosis doesn’t just affect the body; it has profound emotional, psychological, and social implications.
Emotional Struggles
Fear, anxiety, and depression are common feelings for cancer patients and their loved ones. Counseling, support groups, and mindfulness practices can help navigate these challenges.
The Importance of a Support System
Family, friends, and caregivers play a crucial role in a patient’s journey. Whether it’s driving to appointments or simply offering a listening ear, their presence can make a world of difference.
Thriving Beyond Cancer
With advancements in treatment, many people live long, fulfilling lives after cancer. Survivorship programs focus on rehabilitation, nutrition, and mental health to help individuals transition back to their routines.
Preventing Cancer: Steps You Can Take
While not all cancers are preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk.
Healthy Habits
- Quit Smoking: Tobacco is a leading cause of cancer worldwide.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while minimizing processed foods.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise can boost your immune system and maintain a healthy weight.
Routine Screenings
Don’t underestimate the power of early detection. Regular check-ups and screenings can catch abnormalities before they develop into full-blown cancer.
Conclusion: Knowledge Is Power in the Fight Against Cancer
Cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease, but understanding its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options empowers us to make informed decisions. Whether through prevention, early detection, or innovative therapies, the battle against cancer continues to evolve.
By staying educated and proactive, we can support those affected and contribute to the ongoing fight to one day conquer this disease entirely.