Esophageal Cancer: Understanding, Preventing, and Managing This Silent Threat

Esophageal cancer is a critical health condition that often goes unnoticed until it reaches advanced stages. Despite its relatively low profile compared to other cancers, its impact can be devastating for those affected. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything about esophageal cancer—from its causes and symptoms to treatment and prevention strategies.
Understanding Esophageal Cancer: An Overview
The esophagus, a muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach, plays a vital role in the digestive system. Esophageal cancer occurs when cells in this tube grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors.
Types of Esophageal Cancer
- Adenocarcinoma:
This type starts in the glandular cells of the lower esophagus. It is more common in Western countries and is often linked to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and obesity. - Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
Originating in the squamous cells lining the esophagus, this type is more prevalent worldwide, especially in Asia and parts of Africa. Risk factors include smoking and alcohol consumption.
Global Prevalence
Esophageal cancer ranks as the seventh most common cancer globally. While it affects both men and women, men are more likely to develop the disease. The prognosis varies depending on the type, stage, and access to healthcare.
Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
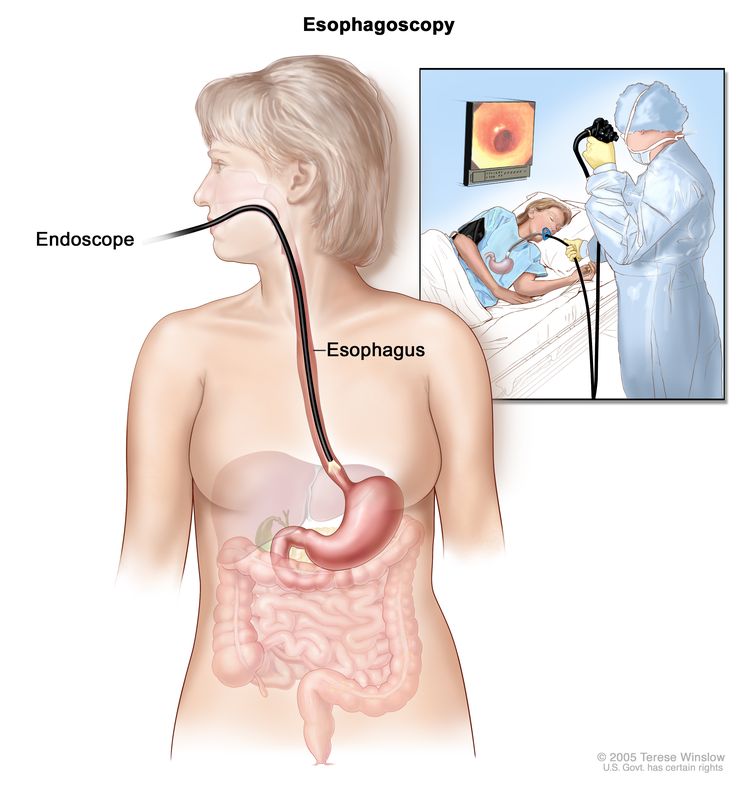
Recognizing the symptoms of esophageal cancer is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Unfortunately, these symptoms often appear once the disease has progressed.
Common Symptoms
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia):
The most common symptom, dysphagia, begins with difficulty swallowing solid foods and progresses to liquids. - Unexplained Weight Loss:
Rapid, unintentional weight loss can be a red flag for esophageal cancer. - Persistent Chest Pain or Discomfort:
Patients may experience burning or pressure-like sensations in the chest or throat. - Chronic Cough or Hoarseness:
Tumors in the esophagus can irritate nearby structures, leading to vocal changes or coughing. - Vomiting or Regurgitation of Food:
As the tumor obstructs the esophagus, regurgitation becomes more frequent.
Why Symptoms Are Often Missed
Esophageal cancer symptoms mimic those of common conditions like GERD or acid reflux. This overlap often leads to delayed diagnoses, making awareness campaigns crucial.
Risk Factors and Causes of Esophageal Cancer
Understanding the risk factors for esophageal cancer is critical for prevention and early detection.
Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking and Tobacco Use:
Smoking increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma significantly. The carcinogens in tobacco damage the esophageal lining over time. - Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive alcohol use is another leading risk factor, especially when combined with smoking. - Dietary Habits:
Diets lacking fruits, vegetables, and essential nutrients can increase the risk of esophageal cancer. Consumption of hot beverages has also been linked to squamous cell carcinoma in certain studies.
Medical Conditions
- Barrett’s Esophagus:
This condition, often caused by long-term GERD, involves changes in the esophageal lining and increases the risk of adenocarcinoma. - Achalasia:
A rare disorder where the esophagus fails to relax properly can lead to food accumulation and an elevated cancer risk. - Obesity:
Excess weight contributes to chronic acid reflux, increasing the likelihood of Barrett’s esophagus and adenocarcinoma.
Genetic Factors
While esophageal cancer is not strongly hereditary, certain gene mutations or family history can predispose individuals to the disease.
Diagnosis of Esophageal Cancer
Detecting esophageal cancer early can improve treatment outcomes significantly. Medical professionals use a combination of symptoms, tests, and imaging to diagnose the disease.
Initial Assessments
- Physical Examination:
A healthcare provider may assess for signs like weight loss, hoarseness, or lymph node swelling. - Medical History:
Chronic GERD, smoking, and other lifestyle habits are key indicators during diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tests
- Endoscopy:
A flexible tube with a camera allows doctors to visualize the esophagus and collect tissue samples (biopsy). - Barium Swallow X-ray:
This imaging test highlights abnormalities in the esophagus, including blockages or irregular shapes. - CT, MRI, or PET Scans:
These imaging techniques help determine the cancer’s stage and whether it has spread to other organs.
Treatment Options for Esophageal Cancer
Treatment for esophageal cancer depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Modern medicine offers several approaches, often used in combination for optimal results.
Surgical Treatments
- Esophagectomy:
This procedure removes part or all of the esophagus, replacing it with a section of the stomach or intestine. - Minimally Invasive Surgery:
Techniques like laparoscopy can reduce recovery times and surgical risks for early-stage cancers.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Chemotherapy:
Drugs are used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors before surgery. - Radiation Therapy:
High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells, often combined with chemotherapy. - Targeted Therapy:
These drugs focus on specific proteins or genes in cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissue. - Immunotherapy:
By enhancing the body’s immune system, this innovative treatment helps combat cancer more effectively.
Coping with Esophageal Cancer: Patient Perspectives
A diagnosis of esophageal cancer can be life-altering, but support systems and coping strategies can make the journey more manageable.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
- Dealing with Fear and Anxiety:
Patients often face overwhelming emotions after diagnosis. Counseling or support groups can provide relief. - Family Support:
Involving loved ones in treatment decisions and care can improve mental health and recovery outcomes. - Mind-Body Practices:
Activities like meditation, yoga, or journaling can help patients stay grounded during treatment.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Dietary Changes:
Soft, nutrient-rich foods are recommended for patients experiencing swallowing difficulties. - Physical Activity:
Gentle exercises, tailored to the patient’s condition, can improve energy levels and overall well-being.
Preventing Esophageal Cancer: Proactive Measures
Prevention is the best strategy when it comes to esophageal cancer. While some risk factors are unavoidable, others can be mitigated through lifestyle changes.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Use:
Reducing these habits can significantly lower the risk of esophageal cancer. - Adopt a Balanced Diet:
Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals. Avoid overly processed or fried foods. - Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Regular exercise and a balanced diet help reduce the risk of obesity-related esophageal cancer.
Medical Monitoring
- Regular Checkups:
Individuals with chronic GERD or Barrett’s esophagus should undergo periodic endoscopies to detect abnormalities early. - Medications for GERD:
Effective management of acid reflux can reduce the risk of Barrett’s esophagus and subsequent cancer development.
The Road Ahead: Hope and Innovation in Esophageal Cancer Research
The future of esophageal cancer treatment is promising, with advancements in medical technology and research paving the way for better outcomes.
Emerging Therapies
- Precision Medicine:
Tailoring treatments to a patient’s genetic profile can improve efficacy and reduce side effects. - Advances in Immunotherapy:
New drugs are being developed to strengthen the immune system’s response to cancer. - Early Detection Tools:
Biomarkers and non-invasive tests are under development to catch esophageal cancer in its earliest stages.
Community Efforts and Awareness
Global campaigns focusing on education, screening, and early diagnosis aim to reduce the burden of esophageal cancer worldwide.
Esophageal cancer is a complex and often aggressive disease, but knowledge and proactive measures can make a significant difference. Whether through lifestyle changes, regular checkups, or supporting ongoing research, we all have a role to play in combating this silent but deadly condition.