RDW Blood Test: Everything You Need to Know

Red Blood Cell Distribution Width (RDW) is a lesser-known but crucial parameter in a standard complete blood count (CBC) test. If your doctor has ever mentioned it, you might have wondered what it signifies and why it’s important. Let’s break down the RDW blood test and why it matters for your health.
What is an RDW Blood Test?
The RDW blood test measures the variation in the size and volume of your red blood cells (RBCs). While most red blood cells are typically uniform in size, some conditions can cause significant variations. RDW highlights this variation, offering insights into potential underlying health issues.
The Basics of RDW
RDW is expressed as a percentage. A normal RDW range typically falls between 11.5% and 14.5%, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory standards. A higher RDW percentage means there’s a greater difference in the size of your red blood cells, which could be a red flag for certain conditions.
Why is RDW Important?
While RDW alone cannot diagnose a specific condition, it is a valuable tool when paired with other blood tests like hemoglobin and mean corpuscular volume (MCV). It can help doctors detect early signs of anemia, nutrient deficiencies, or chronic diseases.
Why is the RDW Test Ordered?
The RDW blood test is often included in routine health check-ups as part of the CBC panel. However, your doctor might specifically focus on RDW if you exhibit symptoms or conditions warranting closer examination.
Common Reasons for an RDW Test
- Symptoms of Anemia
If you feel unusually tired, dizzy, or short of breath, your doctor might suspect anemia. RDW can help identify whether your anemia is due to iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, or chronic disease. - Nutritional Deficiencies
RDW is an excellent marker for spotting nutrient imbalances. Deficiencies in iron, folate, or vitamin B12 can significantly affect the size and health of red blood cells, leading to abnormal RDW levels. - Monitoring Chronic Diseases
RDW can also be an indicator of the progression of chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, or diabetes. Abnormal RDW levels may hint at complications or worsening conditions.
How is the RDW Blood Test Conducted?
The RDW test is a simple and straightforward procedure, usually performed alongside a complete blood count test.
The Process
- Sample Collection
A healthcare provider will draw a small blood sample from a vein in your arm using a sterile needle. - Laboratory Analysis
The blood sample is sent to a lab where automated machines analyze the red blood cells for their size and distribution. - Results Interpretation
The results are usually ready within a few days and are presented alongside other CBC parameters. Your doctor will explain what the results mean in your specific context.
Is It Painful?
The procedure is minimally invasive and might cause slight discomfort at the needle site. However, it’s generally quick and low-risk.
What Do RDW Test Results Mean?
Understanding your RDW results can be a bit tricky, as they are always analyzed alongside other blood parameters. However, here’s a simplified breakdown:
Normal RDW Levels
A normal RDW range indicates that your red blood cells are relatively uniform in size, which is usually a sign of healthy blood function.
High RDW Levels
If your RDW is above the normal range, it could indicate:
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Common in individuals with poor dietary intake or chronic blood loss.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Low levels of folate or vitamin B12 can result in larger and uneven red blood cells.
- Chronic Conditions: Diseases like kidney disease, liver dysfunction, or cardiovascular issues may influence RDW.
Low RDW Levels
Low RDW is rare but might indicate conditions such as hereditary blood disorders or mild anemia that hasn’t yet progressed.
Conditions Linked to Abnormal RDW Levels
RDW is often used as a diagnostic aid to detect various medical conditions. Let’s look at some of the most common links:
1. Anemia
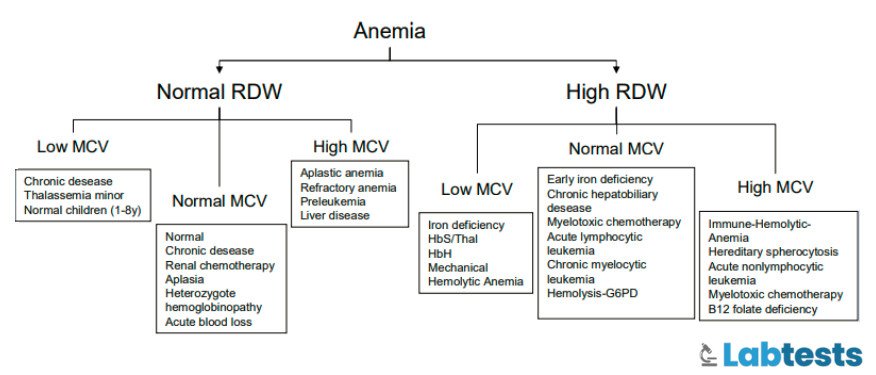
Anemia is one of the primary conditions identified through RDW testing. The type of anemia can often be narrowed down based on RDW and MCV levels:
- High RDW + Low MCV: Iron deficiency anemia.
- High RDW + High MCV: Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
2. Cardiovascular Disease
Research has shown that elevated RDW levels may correlate with a higher risk of cardiovascular events like heart attacks or strokes. This makes it an emerging marker in heart health monitoring.
3. Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease can cause RDW levels to fluctuate due to inflammation affecting red blood cell production.
Can RDW Levels Be Improved?
The good news is that abnormal RDW levels can often be managed through targeted interventions.
Steps to Normalize RDW
- Address Nutritional Deficiencies
A balanced diet rich in iron, folate, and vitamin B12 can improve your red blood cell health. Foods like spinach, beans, meat, and fortified cereals are great choices. - Manage Chronic Conditions
Keeping chronic diseases like diabetes or hypertension under control can stabilize RDW levels over time. - Follow Medical Advice
Always follow your doctor’s recommendations, whether it involves dietary supplements, medications, or lifestyle changes.
When Should You Worry About RDW?
While RDW is a helpful indicator, an isolated abnormal result is not necessarily a cause for alarm.
Discuss With Your Doctor
If your RDW levels are abnormal, your doctor will consider your overall health, symptoms, and other test results before making a diagnosis.
Regular Monitoring
In cases of chronic diseases or ongoing nutritional deficiencies, regular monitoring of RDW can help track progress and adjust treatments accordingly.
Final Thoughts
The RDW blood test is a powerful tool in modern medicine, providing valuable insights into your red blood cell health. While it may not be as commonly discussed as other blood markers, its importance in diagnosing and managing various conditions is undeniable.
Whether you’re undergoing a routine check-up or exploring unexplained symptoms, understanding your RDW results can empower you to take control of your health. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and next steps.