Understanding Pancreatic Elastase: An In-Depth Exploration
The human body is an intricate system where enzymes play a pivotal role in maintaining overall health. Among these enzymes, pancreatic elastase is often overlooked despite its crucial functions in digestion and diagnostic medicine. Let’s dive deep into what pancreatic elastase is, its role, and why it’s essential for our well-being.
What is Pancreatic Elastase?
Pancreatic elastase is an enzyme produced by the pancreas, a vital organ responsible for aiding digestion and regulating blood sugar levels. This enzyme belongs to the serine protease family and is primarily tasked with breaking down elastin, a type of protein found in connective tissues.
Where Does Pancreatic Elastase Come From?
Pancreatic elastase originates from the acinar cells in the pancreas. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the small intestine through pancreatic ducts as part of pancreatic juice. In its inactive form, known as pro-elastase, it requires activation by trypsin to become functional. This activation ensures that the enzyme does not damage the pancreas itself, as elastin is a component of many body tissues.
Role in the Digestive Process
Once in the small intestine, pancreatic elastase targets dietary proteins, specifically those containing elastin, which are typically found in meat and other animal-based foods. By breaking these proteins into smaller peptides, it helps ensure that your body can absorb essential nutrients effectively.
The Importance of Pancreatic Elastase in Health
Pancreatic elastase does more than just digest food; it serves as a critical indicator of pancreatic health. Understanding its levels can provide insights into how well the pancreas is functioning.
Marker of Pancreatic Function
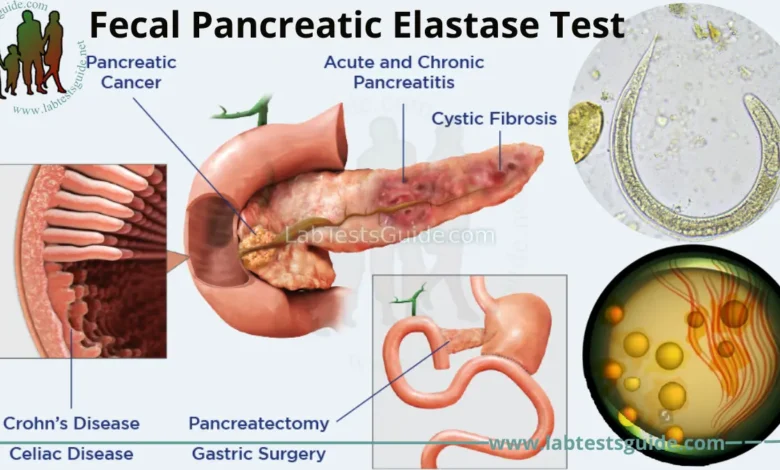
Doctors often measure pancreatic elastase levels through stool tests to evaluate exocrine pancreatic function. Since this enzyme is not degraded during digestion, its concentration in stool directly reflects how effectively the pancreas produces digestive enzymes.
Low levels of pancreatic elastase could indicate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI), a condition where the pancreas fails to produce sufficient enzymes to support digestion. Conditions like chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and pancreatic cancer often cause EPI.
Implications for Overall Health
A deficiency in pancreatic elastase can lead to malabsorption, where the body fails to absorb vital nutrients. This can result in weight loss, diarrhea, and deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), which could compromise immunity, bone health, and vision.
Pancreatic Elastase Tests: How Do They Work?
The pancreatic elastase stool test is a non-invasive diagnostic tool used to assess pancreatic function. It is simple yet highly effective in diagnosing various pancreatic disorders.
How the Test is Performed
The process involves collecting a stool sample, which is then analyzed in a lab to measure the concentration of pancreatic elastase. Results are usually expressed in micrograms of enzyme per gram of stool.
- Normal levels: Above 200 µg/g indicate healthy pancreatic function.
- Mild insufficiency: Levels between 100-200 µg/g suggest a moderate reduction in enzyme production.
- Severe insufficiency: Levels below 100 µg/g indicate significant pancreatic dysfunction.
Who Needs the Test?
This test is often recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms like chronic diarrhea, unexplained weight loss, or bloating, as these could hint at pancreatic issues. It’s also a standard procedure for those diagnosed with chronic conditions like diabetes or cystic fibrosis, which may impair pancreatic function over time.
Factors Affecting Pancreatic Elastase Levels
Several factors can influence pancreatic elastase levels, and understanding them is vital for accurate diagnosis and management of pancreatic health.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Diseases like pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or cystic fibrosis can drastically lower pancreatic elastase production. Additionally, diabetes, particularly Type 1, is linked to reduced pancreatic function, as the disease affects the pancreas’ ability to produce both enzymes and insulin.
Lifestyle Choices
Unhealthy diets high in processed foods, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can weaken the pancreas over time, leading to reduced enzyme production. Stress and a sedentary lifestyle may also indirectly affect pancreatic health, exacerbating conditions like EPI.
Aging
As we age, the pancreas naturally becomes less efficient. This decline may cause a subtle reduction in pancreatic elastase levels, even in healthy individuals.
Managing and Improving Pancreatic Elastase Levels
If your pancreatic elastase levels are low, addressing the root cause is essential. Thankfully, there are multiple ways to manage and improve enzyme production.
Medical Interventions
Doctors may prescribe pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) to individuals with EPI. These supplements contain enzymes, including pancreatic elastase, to aid digestion and improve nutrient absorption.
Additionally, treating underlying conditions like diabetes or pancreatitis can help stabilize pancreatic function and enzyme levels.
Dietary Changes
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support pancreatic health. Avoiding excessive fats and sugars reduces the pancreas’s workload, preventing further damage.
Incorporating probiotics and prebiotics may also improve gut health, which works synergistically with enzymes to optimize digestion.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and managing stress are lifestyle changes that can significantly benefit pancreatic function. Regular exercise and staying hydrated also contribute to overall digestive health.
The Future of Pancreatic Elastase Research
Pancreatic elastase is not just a digestive enzyme; it holds promise in advancing medical diagnostics and treatment. Ongoing research continues to explore its broader applications in health and disease management.
Innovations in Diagnostics
Scientists are developing more sensitive and specific tests to measure pancreatic elastase levels. These advancements aim to detect pancreatic dysfunction at earlier stages, enabling timely intervention.
Potential Therapeutic Uses
Emerging studies suggest that manipulating enzyme levels could play a role in treating certain gastrointestinal disorders. Research into enzyme supplementation is expanding, offering hope for individuals with severe digestive issues.
Conclusion: Why Pancreatic Elastase Deserves Attention
Pancreatic elastase is a small but mighty enzyme that serves as both a digestive aid and a diagnostic marker. Its role in breaking down proteins is critical for nutrient absorption, and its measurement offers valuable insights into pancreatic health.
Whether you’re experiencing symptoms of pancreatic dysfunction or simply want to maintain optimal digestion, understanding and supporting your pancreatic elastase levels can have a profound impact on your overall well-being. Taking proactive steps like adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking timely medical advice can go a long way in preserving pancreatic health for years to come.