Understanding Esophageal Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
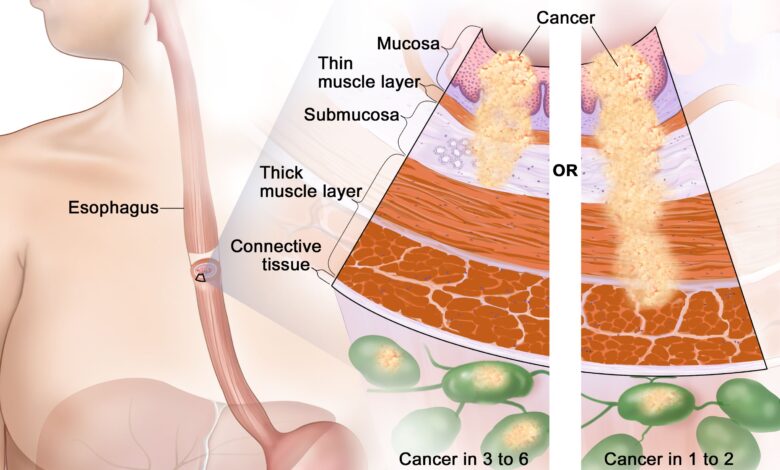
Esophageal cancer is a serious health condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach. Despite its complexity, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and improved outcomes. Let’s delve into everything you need to know about this condition in a casual yet expert tone.
What Is Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer occurs when malignant cells develop in the lining of the esophagus. The two primary types of this cancer are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma affects the upper and middle parts of the esophagus, while adenocarcinoma is more common in the lower part.
The esophagus plays a vital role in digestion, carrying food from the throat to the stomach. Cancer in this area disrupts the process, leading to complications such as difficulty swallowing and pain. This condition is relatively rare but has a high mortality rate when diagnosed late.
Understanding esophageal cancer is the first step in combating it. Awareness of the risk factors and early symptoms can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment.
What Causes Esophageal Cancer?

Esophageal cancer doesn’t develop overnight. It is often the result of long-term exposure to certain risk factors or underlying medical conditions.
1. Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Smoking damages the lining of the esophagus, increasing cancer risk. Excessive alcohol consumption also irritates the esophagus, creating a similar effect.
- Poor Diet: Diets lacking fruits, vegetables, and essential nutrients can weaken the esophageal lining, making it more susceptible to cancer.
2. Medical Conditions
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux can lead to Barrett’s esophagus, a condition where the esophageal lining changes, significantly increasing cancer risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on the stomach, contributing to acid reflux and other esophageal issues.
3. Environmental and Genetic Factors
- Exposure to Carcinogens: Workplace exposure to harmful chemicals can heighten cancer risk.
- Genetics: A family history of esophageal cancer can predispose individuals to the disease.
Recognizing these causes is essential for prevention. While some factors, like genetics, are unavoidable, lifestyle modifications can dramatically reduce your risk.
Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
Early detection is challenging because symptoms often appear in advanced stages. However, being aware of the warning signs can make a life-saving difference.
1. Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
One of the earliest symptoms, dysphagia, makes it hard to swallow food or drinks. Patients may feel like food is getting stuck in their throat, leading to discomfort or even pain.
2. Unintended Weight Loss
Esophageal cancer can cause significant weight loss due to difficulty eating and a reduced appetite. If you’re losing weight without trying, it’s worth consulting a doctor.
3. Chest Pain and Heartburn
Persistent chest pain or a burning sensation, often mistaken for severe heartburn, can be a symptom of esophageal cancer.
4. Hoarseness and Coughing
A hoarse voice or chronic cough, especially if unrelated to a cold or flu, could indicate something more serious.
Other symptoms may include fatigue, vomiting, and even hiccups in some cases. Prompt medical attention is crucial if you experience these symptoms consistently.
How Is Esophageal Cancer Diagnosed?
The diagnosis process typically involves multiple tests to confirm the presence and stage of cancer.
1. Endoscopy
A thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the esophagus to check for abnormalities. This is one of the most common diagnostic tools.
2. Biopsy
If suspicious tissue is found during an endoscopy, a small sample is taken for laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
3. Imaging Tests
Techniques such as CT scans, PET scans, or barium X-rays provide detailed images, helping doctors assess the cancer’s spread.
Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for planning effective treatment and improving survival rates.
Treatment Options for Esophageal Cancer
Treatment for esophageal cancer depends on the stage, location, and overall health of the patient. Modern medicine offers several options to combat this disease effectively.
1. Surgery
- Esophagectomy: This procedure involves removing the affected portion of the esophagus and reconstructing it using parts of the stomach or intestine.
- Endoscopic Surgery: For early-stage cancer, minimally invasive techniques may be used to remove cancerous cells.
2. Radiation Therapy
High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. Radiation therapy is often combined with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or surgery, for better outcomes.
3. Chemotherapy
Drugs are administered to destroy cancer cells, either before surgery to reduce tumor size or after surgery to kill remaining cells.
4. Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
- Targeted Therapy: This involves using drugs designed to attack specific proteins or genes in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: This boosts the immune system to fight cancer more effectively.
Each treatment plan is tailored to the individual, considering factors like age, cancer stage, and personal preferences.
Prevention: Can Esophageal Cancer Be Avoided?
While not all cases are preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly lower your risk.
1. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Eliminating tobacco and reducing alcohol intake are two of the most impactful steps you can take.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Regular exercise and a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can prevent obesity and related conditions like GERD.
3. Manage Acid Reflux
If you have GERD, seek treatment early to avoid complications like Barrett’s esophagus. Medications and lifestyle changes can help.
4. Regular Screenings
For those at high risk due to family history or existing conditions, routine screenings can help catch abnormalities early.
Prevention requires consistency and commitment, but the results are worth the effort.
Living with Esophageal Cancer
A diagnosis of esophageal cancer can be life-altering, but many patients manage to live fulfilling lives through a combination of treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
1. Emotional Support
Counseling and support groups can help patients cope with the emotional toll of cancer. Family and friends also play a vital role in providing comfort and encouragement.
2. Nutrition and Diet
Eating soft, nutrient-rich foods can ease swallowing difficulties and ensure proper nourishment during treatment. Consulting a dietitian can provide personalized guidance.
3. Regular Follow-Ups
Post-treatment care involves regular check-ups to monitor for recurrence and manage any side effects.
Living with esophageal cancer is challenging but manageable with the right resources and support.
Conclusion
Esophageal cancer is a formidable condition, but early detection and proper treatment can make all the difference. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward prevention and care.
Remember, awareness saves lives. Whether it’s quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet, or seeking timely medical advice, every effort counts in the fight against esophageal cancer.