Cancers: Understanding the Disease, Types, and Prevention Strategies

Cancers, a word that often evokes fear and uncertainty, is a complex group of diseases that affect millions worldwide. Despite advancements in medical science, it remains one of the leading causes of death globally. However, understanding cancer’s intricacies, its types, and preventive measures can empower individuals to take proactive steps toward a healthier life.
What is Cancer? The Basics of the Disease
Cancer arises when cells in the body grow uncontrollably, forming masses or tumors that may invade surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body (metastasis). This unregulated cell growth disrupts the body’s natural processes, leading to significant health complications.
The Mechanisms Behind Cancer
At its core, cancer is a genetic disease caused by mutations in DNA. These mutations can be inherited, occur due to environmental factors, or result from random cellular processes. They affect the genes that regulate cell growth and repair, leading to the development of malignant cells.
The Difference Between Benign and Malignant Tumors
Not all tumors are cancerous. Benign tumors are non-invasive and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant tumors, however, are aggressive, invade nearby tissues, and have the potential to metastasize, posing a greater health risk.
How Cancer Spreads
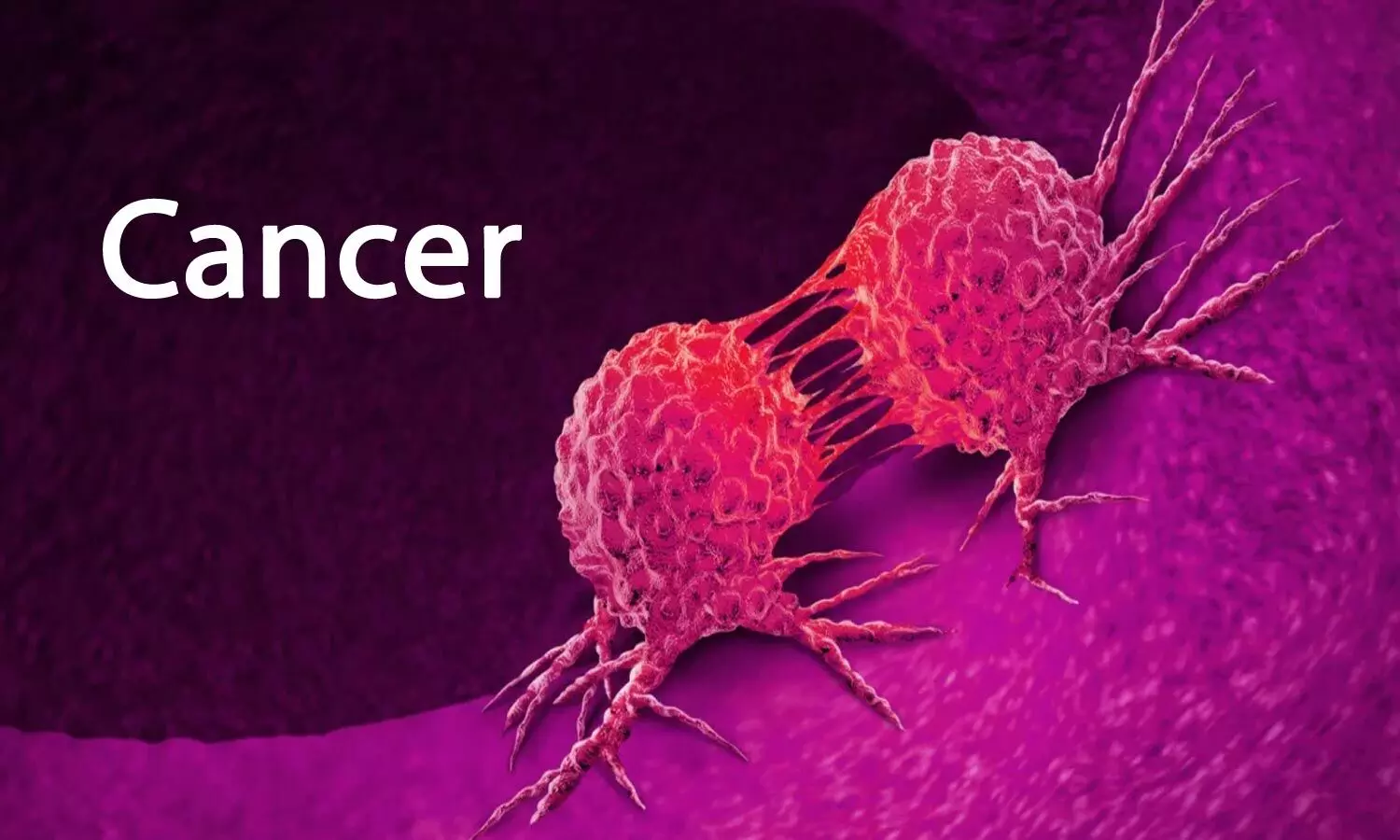
Cancer spreads through a process known as metastasis, where malignant cells break away from the primary tumor, travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, and establish new tumors in other parts of the body. This is one of the reasons why early detection is crucial.
Common Types of Cancer and Their Impact
Cancer isn’t a single disease but a collection of related conditions. Each type of cancer is unique in its symptoms, progression, and treatment approach.
1. Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most common and deadliest cancers globally. It is primarily caused by smoking, although non-smokers can develop it due to factors like air pollution and exposure to carcinogens.
- Symptoms: Persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and weight loss.
- Prevention: Avoid smoking, reduce exposure to pollutants, and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
2. Breast Cancer
Breast cancer affects both men and women, though it is significantly more common in women. Early detection through regular screenings like mammograms can save lives.
- Symptoms: Lumps in the breast, changes in breast shape, and unusual discharge.
- Prevention: Regular screenings, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol intake.
3. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer primarily affects older men and is often detected through routine screenings.
- Symptoms: Difficulty urinating, blood in urine, and pelvic pain.
- Prevention: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables, regular exercise, and annual check-ups.
4. Colorectal Cancer
This cancer affects the colon and rectum and is linked to dietary habits, age, and genetic predisposition.
- Symptoms: Changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, and abdominal discomfort.
- Prevention: A fiber-rich diet, regular exercise, and colonoscopy screenings after age 50.
Early Detection: Why It Matters
Early detection is a critical factor in cancer treatment. Identifying cancer in its initial stages often improves treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Screening Tests
Regular screenings can detect cancers like breast, cervical, and colorectal cancers early. Tests such as mammograms, Pap smears, and colonoscopies are highly effective.
Self-Examinations
Self-awareness and routine self-examinations can help individuals notice early signs of abnormal changes in their bodies. For example, regular breast self-exams can help identify unusual lumps.
Genetic Testing
For individuals with a family history of cancer, genetic testing can reveal predispositions, enabling proactive monitoring and preventive measures.
Cancer Treatments: Navigating Options
Cancer treatment has evolved significantly, offering patients various options tailored to their specific diagnosis.
1. Surgery
Surgical removal of tumors is often the first line of treatment. It is most effective when the cancer is localized and has not metastasized.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. While effective, it often comes with side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and hair loss.
3. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. It is often used in combination with other treatments.
4. Immunotherapy
This innovative approach boosts the body’s immune system to recognize and fight cancer cells. Immunotherapy has shown promise, particularly in treating aggressive cancers like melanoma.
5. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are designed to attack specific genetic mutations within cancer cells, sparing healthy cells and reducing side effects.
Prevention Strategies: Reducing Your Risk
While not all cancers can be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly lower your risk.
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall health. Limiting processed foods and red meats can also reduce cancer risk.
2. Stay Physically Active
Regular exercise not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also lowers the risk of cancers such as breast and colon cancer.
3. Avoid Tobacco
Tobacco use is a leading cause of cancers, including lung, throat, and mouth cancers. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to reduce your cancer risk.
4. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake is linked to several cancers, including liver, breast, and esophageal cancer. Moderation is key.
5. Protect Your Skin
Skin cancer, including melanoma, can be prevented by minimizing sun exposure, wearing sunscreen, and avoiding tanning beds.
The Emotional and Mental Impact of Cancer
Cancer affects not only the body but also the mind and spirit. Patients often face emotional challenges such as anxiety, depression, and fear of the unknown.
The Role of Support Systems
Having a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals can make a significant difference. Support groups and counseling can provide emotional relief and practical advice.
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and improve overall well-being during and after treatment.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Cancer Research
The fight against cancer is far from over, but advancements in research are bringing hope. From personalized medicine to AI-driven diagnostics, the future looks promising.
Breakthroughs in Treatment
Innovations like CAR T-cell therapy and CRISPR gene editing are revolutionizing cancer treatment, offering more precise and effective solutions.
The Role of Technology
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are enhancing diagnostic accuracy and predicting patient outcomes, enabling earlier and more effective interventions.
Global Collaboration
International efforts to share data and resources are accelerating progress in understanding and treating cancer on a global scale.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Health
Cancer remains a formidable challenge, but understanding its mechanisms, staying vigilant about early detection, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can make a significant difference. While medical science continues to advance, the power of prevention, education, and support should not be underestimated. Stay informed, prioritize your health, and remember that early action can save lives.